PURPOSE. To compare the photochemical properties of UV filter molecules present in the human lens (kynurenine, KN; 3-hy- droxykynurenine, 3OHKN; 3-hydroxykynurenine O-gluco- side, 3OHKG; 4-(2-aminophenyl)-4-oxobutanoic acid, AHA; and glutathionyl-kynurenine, GSH-KN) with the use of the following parameters: excited singlet lifetime, fluorescence quantum yield, triplet quantum yield, photodecomposition quantum yield.
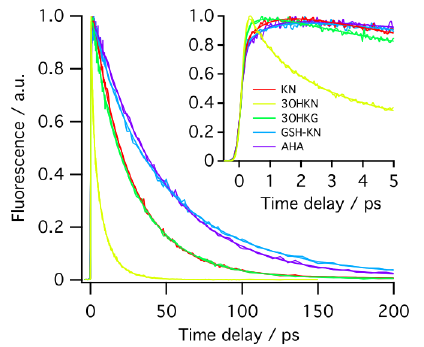
METHODS. The excited singlet lifetimes were measured with the use of fluorescence upconversion (time resolution, 210 fs) and pump-probe transient absorption (time resolution, 200 fs) methods. The fluorescence quantum yields were determined relative to an aqueous solution of quinine bisulfate. The triplet quantum yields were measured with the use of nanosecond laser flash photolysis. The photodecomposition quantum yields were determined by steady state photolysis followed by the high-performance liquid chromatography analysis.
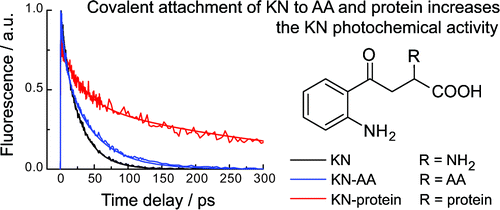
RESULTS. The secondary UV filters—AHA and GSH-KN are better photosensitizers than the primary ones -KN, 3OHKN and 3OHKG: the singlet state lifetimes of the secondary UV filters are longer, and the quantum yields of fluorescence and triplet state formation are higher.
CONCLUSIONS. With aging, the ratio primary/secondary UV filters in the human lens decreases from approximately 10:1 to 2:1. The obtained results demonstrate that the quality of the secondary UV filters is inferior compared to the primary ones, which may result in a higher susceptibility of old lenses to UV light. That might be an important factor for the development of the age-related cataract.